Welcome to the fascinating realm of PCB (Printed Circuit Board) assembly, an integral part of the electronics industry, specifically in pcb assembling. This intricate field is the backbone of virtually all electronic devices, from smartphones to spacecraft. Ready to delve into the complexities and marvels of PCB assembly? Strap in as we unravel its mysteries and explore its intricacies in the world of pcb assembling.
Key Takeaways
- PCB assembly is a meticulous process involving material acquisition, SMT and DIP processing, testing, and integration of technologies like THT, supported by the crucial use of solder paste for component connections.
- Soldering techniques like reflow and wave soldering are essential for creating strong connections and securing THT components, respectively, while inspection methods like AOI, X-Ray, and functional testing ensure quality control.
- Emerging technologies like automation and Industry 4.0 are significantly impacting PCB assembly, optimizing consistency and efficiency, while preparation practices like DFM and substrate selection are fundamental to successful assembly.
Understanding PCB Assembly
The PCB assembly process, including smt assembly, consists of the following steps:
- Acquisition of materials
- SMT (Surface Mount Technology) chip processing
- DIP (Dual In-line Package) plug-in processing
- PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) testing
These steps culminate in a finished product, including all the components.
We will explore the role of solder paste, the precision of component placement, and the integration of Through Hole Technology (THT) in this segment.
The Role of Solder Paste in PCB Assembly
Solder paste, the unsung hero of PCB assembly, plays a critical role in establishing robust connections between components and the board. It is like the glue that holds the puzzle pieces together, ensuring both electrical integrity and mechanical stability. This paste comprises solder powder, typically consisting of 96.5% tin, 3% silver, and 0.5% copper, combined with a flux to form a uniform creamy mixture.
Applying solder paste during PCB assembly involves a stencil printer that spreads the paste evenly across the stencil, depositing it onto designated areas of the PCB for component placement.
Placing Components with Precision
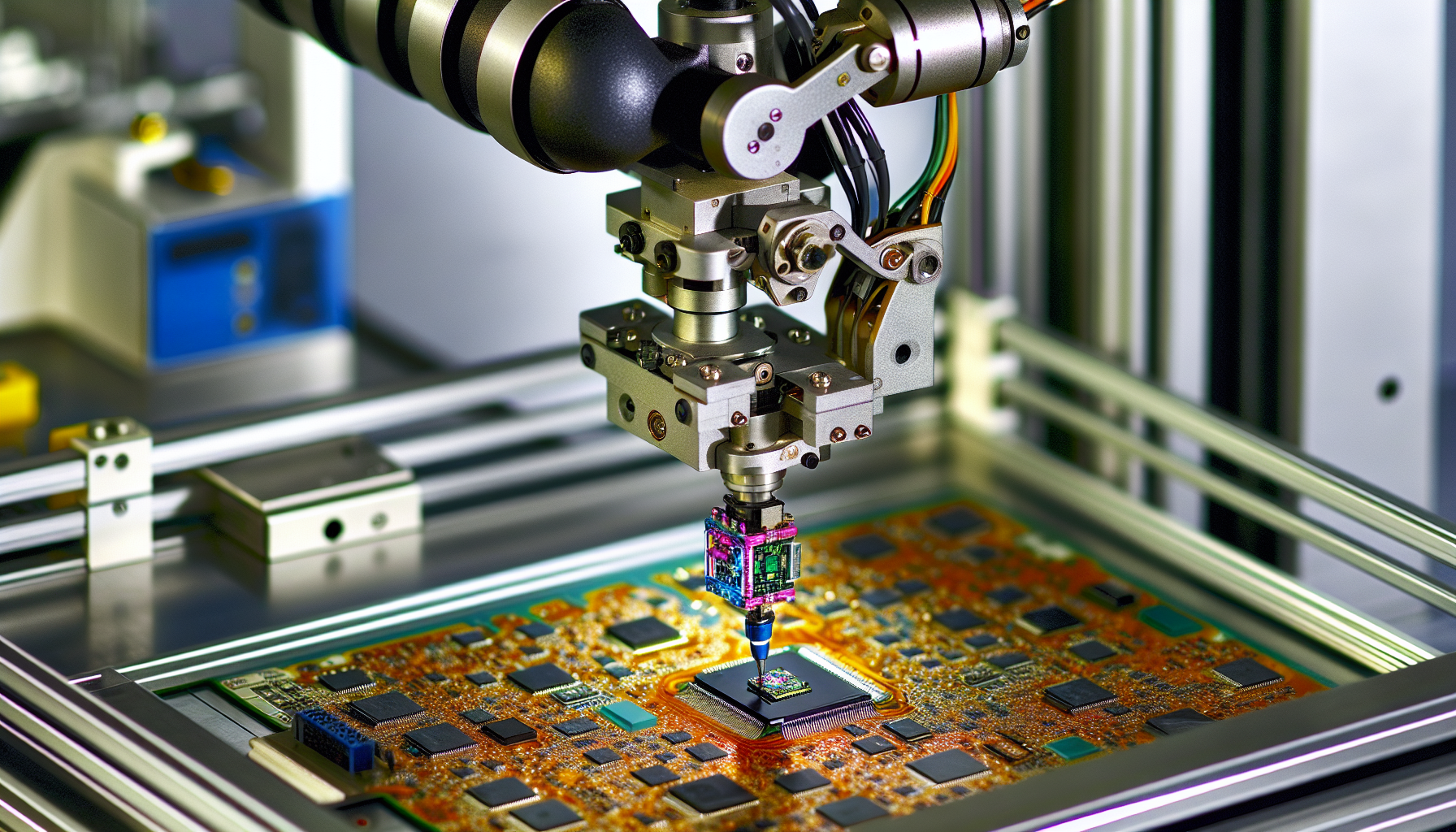
Just as a skilled artist meticulously places each stroke on a canvas, precision is key in placing electronic components on a PCB. Enter the pick-and-place robot, the artist of the PCB assembly world. This robot carefully picks the components from its vacuum grip and accurately positions them on top of the solder paste.
These robots provide significant advantages over manual methods, offering consistent, rapid, and precise component placement.
Through Hole Technology (THT) Integration
In the grand orchestra of PCB assembly, Through Hole Technology (THT) plays a vital role. THT is a traditional method where components are inserted with leads into drilled holes on the PCB, commonly used for larger, high-power, or high-voltage parts alongside SMT. Though this method may seem outdated compared to the automated placement of SMT components, it holds its ground for certain applications, proving that sometimes, old is gold.
Intricacies of the Soldering Process
Soldering in PCB assembly is a fine art, involving a delicate balance of heat and timing to create strong, reliable connections. We shall investigate reflow and wave soldering techniques, focusing on their unique benefits and applications.
Reflow Soldering: Creating Strong Connections
Reflow soldering is akin to a symphony, involving a sequence of stages that come together to create a harmonious end product. This process involves pre-heating the components, PCB, and solder paste to form acceptable solder joints, then melting the solder without causing any damage, thereby ensuring strong connections in PCBs. It’s a finely tuned process that contributes significantly to the reliability of the assembly.
Wave Soldering: Efficiently Securing THT Components
Wave soldering is an automated technique used for soldering THT components, as opposed to manual soldering methods. It involves the use of a wave of molten solder that is directed onto the bottom layer of the PCB where the components’ leads are located, allowing for the simultaneous soldering of all the pins. This process is particularly efficient for soldering electronic components in large quantities.
This method is like a well-oiled production line, efficiently securing THT components onto PCBs.
Inspection and Quality Control Measures
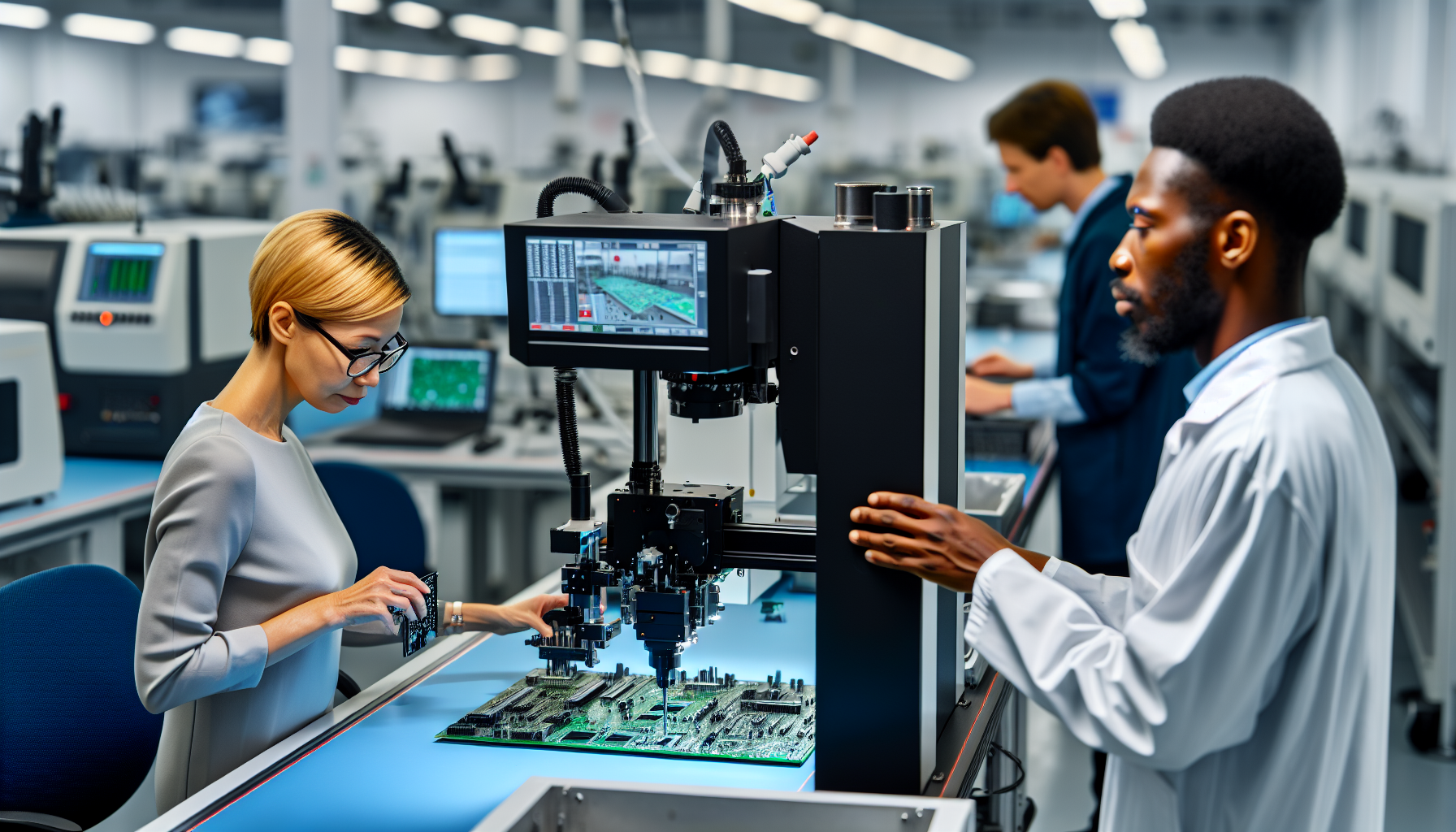

Like a well-written book, a well-assembled PCB board requires thorough proofreading, or in this case, inspection and quality control. These processes are essential for identifying any flaws, ensuring a defect-free final product. The final inspection plays a crucial role in achieving this goal.
We will examine the use of Automatic Optical Inspection (AOI), X-Ray Inspection, and functional testing in PCB assembly in this part.
Automatic Optical Inspection (AOI)
In the world of PCB assembly, the AOI is the equivalent of a spell-checker. This machine-based inspection technique examines the device under test for a range of defects, from major issues such as missing components to quality defects like component misalignment, ensuring the verification of PCB quality and functionality.
X-Ray Inspection for Hidden Faults
Like an X-ray scan revealing hidden fractures, X-Ray Inspection in PCB Assembly is used to detect concealed flaws within a circuit board. It uses X-ray radiation to penetrate the PCB and acquire intricate images of its internal components.
Functional Testing: The Final Verdict
Functional testing in PCB assembly is the final gatekeeper, verifying proper functionality and absence of defects in the manufactured part. It’s like a final exam that determines if the PCB is ready for the real world.
The Different Faces of PCB Assembly Services
Like a one-stop shop, PCB assembly services offer a variety of solutions to meet diverse needs. From prototyping and short-run assemblies to full-scale production runs, each service caters to specific requirements and volume needs.
Prototyping and Short-Run Assemblies
Imagine you could test-drive a car before it’s fully built. That’s what prototyping in PCB assembly is like. It is the creation of an initial version of a PCB design to provide visual assistance, enable thorough testing, and minimize the time and resources spent on full-scale production.
Short-run assemblies, on the other hand, involve the fabrication of printed circuit boards in small quantities, typically ranging from 10 to 100 pieces, which can also include mixed assembly processes.
Full-Scale Production Runs
Full-scale production runs in PCB assembly are the grand finale. They involve the mass production of PCBs, using automated machinery or hand soldering techniques to place and solder components onto the board. This stage of the PCB assembly process is all about scale, speed, and cost-effectiveness.
Advanced Technologies Influencing PCB Assembly
Like a wave of innovation, advanced technologies have swept across the landscape of PCB assembly, bringing about transformative changes. In this part, we will study the influence of automation and Industry 4.0 on the assembly process and its potential for creating new opportunities.
Automation in PCB Assembly: A Game Changer
Automation in PCB assembly is like an artist who never tires, continuously creating masterpiece after masterpiece. It has enhanced the precision and consistency of PCB assembly, making it a game changer in the industry.
The Impact of Industry 4.0 on Circuit Assembly
The advent of Industry 4.0 has brought about a revolution in the field of circuit assembly. This fourth industrial revolution, characterized by the fusion of cyber-physical systems and advanced technologies, has enabled instantaneous exchange of alterations between mechanical assembly and circuit board design, enhancing production efficiency.
Preparing for PCB Assembly: Best Practices
Preparation is key in any endeavor, and PCB assembly is no exception. In this segment, we will navigate you through the best practices for preparing for PCB assembly, which includes Design for Manufacturability (DFM) and selecting the suitable substrate material.
Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) in PCB Assembly is like a preventive health check-up. It identifies and addresses any potential flaws or errors in the PCB to prevent malfunctions during the fabrication and assembly process.
Selecting the Right Substrate Material
Choosing the right substrate material for your PCB is like selecting the right foundation for your house – it’s crucial to its stability and performance. Various types of substrate materials are available, each with its unique properties and applications.
Finishing Touches: Post-Assembly Procedures
A well-assembled PCB, like a beautifully baked cake, requires some finishing touches. Post-assembly procedures including:
- Cleaning
- Inspection
- Packaging
- Shipping
are crucial to deliver a defect-free final product.
Cleaning and Inspection Post-Assembly
Just as a good chef cleans the kitchen after cooking, a good PCB assembler ensures that the PCB is cleaned and inspected after assembly. This step is essential to eliminate contaminants and flux residues that may result in failures.
Packaging and Shipping
Packaging and shipping are the final steps in the PCB assembly process, ensuring that the PCBs reach their destination safely. Proper handling and protection during transit are crucial to prevent any damage or functionality issues.
Summary
From understanding the basics of PCB assembly to exploring the impact of advanced technologies, we’ve journeyed through the intricate and fascinating world of PCB assembly. By implementing best practices and leveraging the advancements of Industry 4.0, we can ensure the production of high-quality, reliable PCBs. So, are you ready to conquer the world of PCB assembly?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is PCB assembly process?
The PCB assembly process includes steps such as solder paste application, component assembly, soldering, board testing, and final inspection. It involves assembling components onto the printed circuit board through a series of specific procedures.
How much does it cost to get a PCB assembled?
The average cost of PCB assembly ranges from $0.02 to $0.05 per square inch, taking design complexity and labor into consideration. Keep in mind that this cost can fluctuate due to factors like labor rates and overhead expenses.
What is the role of a PCB assembly?
The role of a PCB assembly is to integrate electronic components into a defined space, serving as the central hub of an electronic circuit and providing insulation for other electrical components, allowing them to be safely connected to a power source.
What is the difference between PCB fabrication and PCB assembly?
The main difference between PCB fabrication and PCB assembly is that fabrication involves creating the bare PCB, while assembly involves adding components to create a functional circuit. Therefore, PCB fabrication creates the bare PCB, while assembly adds components to create a functional circuit.
What is the PCB assembly main?
The main purpose of a PCB assembly is to hold electronic circuits together using a flat sheet of insulating material with a copper foil layer, along with electroplated copper conductors and vias to create connections between components. This ensures the proper functioning of electronic devices.

